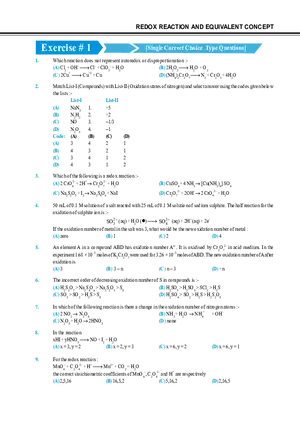
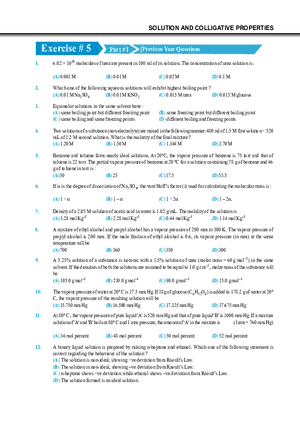Answer Key
Chemistry Chapter 12 Solutions Part 2
-
University:
Kentucky State University -
Course:
CHE 101 | General Chemistry I Academic year:
2020
-
Views:
35
Pages:
4
Author:
Sean Horton
Related Documents
- Determining the Chemical Formula of a Substance
- Molarity of Solution
- Solution Form Cell with Non-Reacting Electrodes (Inert/Inactive)
- Corrosion - Study Notes
- Aromatic Compounds
- Chemistry Hw Review
- Renal Acid - Base Balance
- Anterior Pituitary Study Note
- Balancing Redox Reaction Equations
- Uses of Volta Cells
- Electrochemical Cells
- P-Block Notes
- Reaction Rates and Mechanisms
- Reaction Coefficient
- Mollar Mass - Study Notes
- Mole Concept - Notes
- Molar Volume of Gas
- Stoichiometry: Limiting Reagent Calculations
- Determining Hydrate Chemical Formulas
- Compound Stoichiometry
Report
Tell us what’s wrong with it:
Thanks, got it!
We will moderate it soon!
Report
Tell us what’s wrong with it:
Free up your schedule!
Our EduBirdie Experts Are Here for You 24/7! Just fill out a form and let us know how we can assist you.
Take 5 seconds to unlock
Enter your email below and get instant access to your document