Lecture Note
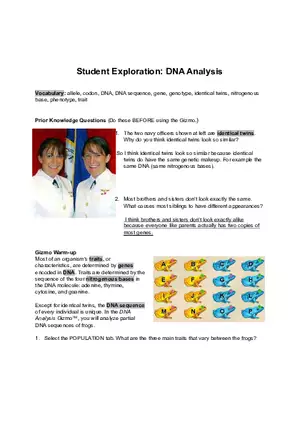
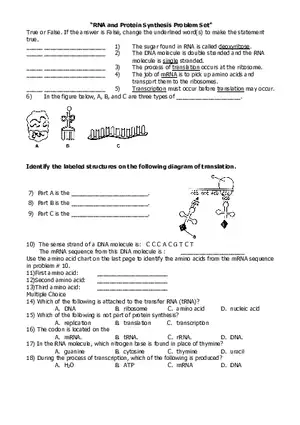
Enzymes Lecture Note
-
University:
Cameron University -
Course:
1004 | General Biology Academic year:
2024
-
Views:
63
Pages:
1
Author:
Clint W.
Related Documents
- Arts and Science 3CF3
- Course and Relations of Rectum
- Lecture Note About Features of Colon
- The Colon - Structure, Function, and Blood Supply
- Anatomy and Functions of Duodenum
- Surface and Features of Stomach
- Principles of Biology. Chapter 1 Lecture Notes
- Liver-features and Supplies
- Muscles and supplies of Rectum
- General Features of Small Intestine
- Biology Lecture Note: Parts of Stomach
- Lecture Note: Lobes of Liver
- Palatine Tonsils - Study Note
- Structures of Pharynx
- Oral Cavity - Lecture Note
- Definition of Digestive System
- Topic 13 Ecology - Class Note
- Topic 12 Animals - Study Note
- Topic 11 Plants - Lecture Note
- Gram Positive & Negative, ABX MicroBio
Enzymes Lecture Note

New Documents from this Course
Report
Tell us what’s wrong with it:
Thanks, got it!
We will moderate it soon!
Report
Tell us what’s wrong with it:
Free up your schedule!
Our EduBirdie Experts Are Here for You 24/7! Just fill out a form and let us know how we can assist you.
Take 5 seconds to unlock
Enter your email below and get instant access to your document