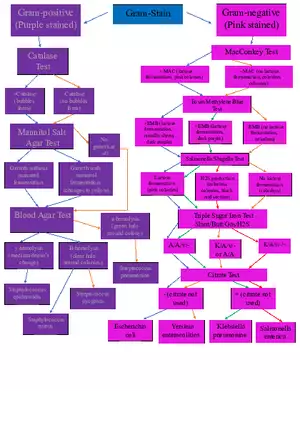
Lecture Note
Pathological Calcification
-
University:
University of South Florida -
Course:
MCB 3020 | General Microbiology Academic year:
2020
-
Views:
413
Pages:
1
Author:
Firstek
Related Documents
- Classification of Inflammatory Mediators by Origin
- Points About Edema
- Cubital Anastomosis : Anastomosis Around Elbow
- Brachial Plexus - Study Notes
- Bones of Hand - Hints
- Abdominal Aorta - Exam Prerp Notes
- 4th Ventricle of Brain: Floor
- Toxoplasma
- Reversible VS Irreversible Injury
- Repair VS Regeneration
- Proteinuvia
- Arterial VS Venous Thrombi. Antimortem VS Postmortem Thrombi
- Comparison of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense and T.b. rhodesiense
- Lab Diagnosis
- Immunity (Notes + Marking)
- Healing of Skin Wounds
- Factors That Influence Infarct Development
- Diphylobothrium Lecture Notes
- Cryptosporidium Lecture Notes
Report
Tell us what’s wrong with it:
Thanks, got it!
We will moderate it soon!
Report
Tell us what’s wrong with it:
Free up your schedule!
Our EduBirdie Experts Are Here for You 24/7! Just fill out a form and let us know how we can assist you.
Take 5 seconds to unlock
Enter your email below and get instant access to your document