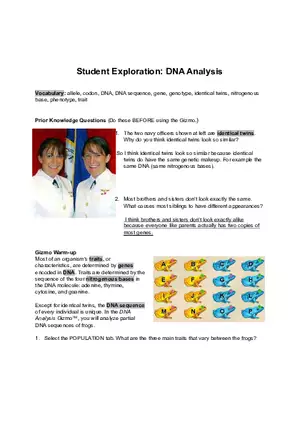
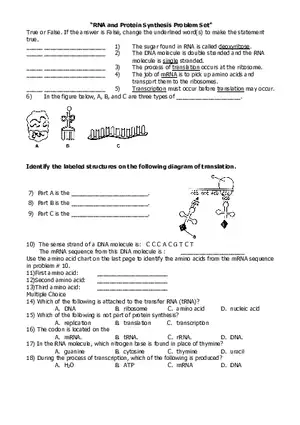
Lecture Note
Cloning
-
University:
Cameron University -
Course:
1004 | General Biology Academic year:
2023
-
Views:
303
Pages:
1
Author:
Clint W.
Related Documents
- Disturbance On Excretion System
- Structure And Function Cell
- Transport Through Membrane
- Lecture Notes - Transport Through Membrane
- Human Physiology Mechanism Of O2 And Co2 In Human Body
- Gametes Formation Process
- Excretion System On Man
- Excretion System On Animal
- Endocrine System - Lecture Note
- Center Nerve System
- Weekly Task Digestive System In Curd Animals Breed
- Breathing Mechanism
- Human Respitary Organs
- Classification Of Bacteria
- Assignment Healty, Nutritions And Balance Food
- Root And Steam Structure
- Leaf Anatomy And Morphology
- Flower Anatomy And Structure
- Differences Of Animal Cell And Plant Cell
- Human Tissue - Lecture Note
Cloning

New Documents from this Course
Report
Tell us what’s wrong with it:
Thanks, got it!
We will moderate it soon!
Report
Tell us what’s wrong with it:
Free up your schedule!
Our EduBirdie Experts Are Here for You 24/7! Just fill out a form and let us know how we can assist you.
Take 5 seconds to unlock
Enter your email below and get instant access to your document